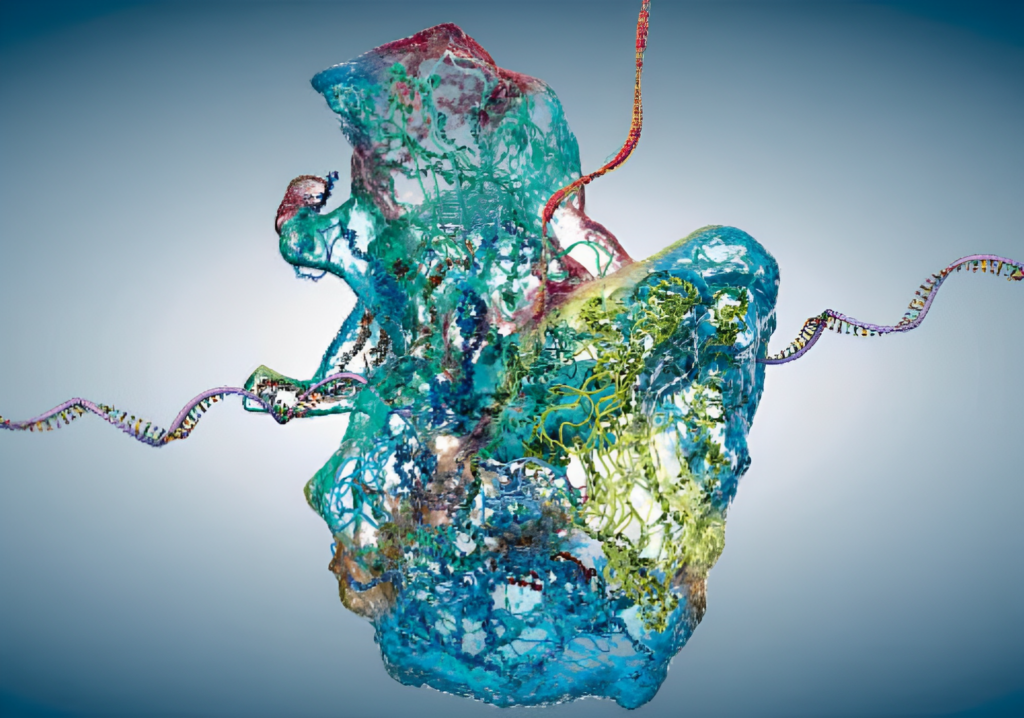
In a development scientists have made an achievement by successfully creating self replicating ribosomes outside of living cells. This accomplishment represents a step, in the ambitious endeavor of constructing artificial cells that can replicate themselves from scratch. It not sheds light on the origins of life. Also opens up new possibilities for revolutionary advancements in the field of biotechnology.
The Enigma of Ribosomes:
At the core of all life forms ribosomes serve as factories where genetic information is translated into the complex machinery responsible for protein synthesis. However in order to understand how life originated many scientists propose that ribosomes must have had the ability to assemble and replicate long before cells came into existence. This concept is both audacious and fascinating.
The Intricacy Involved:
The crux of this matter lies in the process of self replication. Achieving this requires the convergence of, around 200 types of molecules, which has long eluded scientists working within laboratory settings.
The Seven-Year Odyssey:
For a span of seven years Wataru Aoki and his team, from Kyoto University in Japan dedicated their efforts to perfecting the conditions for ribosomes to replicate themselves outside of a cell based environment. Their path involved a series of trials and experiments aimed at optimizing the reaction mixture ultimately leading them to unlock the secrets, behind self replication.
200 types of molecules are involved in ribosome self-replication
The Experimental Breakthrough:
Their setup involved introducing DNA coding for components and utilizing ribosomes obtained from E. Coli cells within a controlled environment. To this mixture they added a modified version of cytoplasm extracted from E. Coli cells. With the assistance of intelligence the researchers diligently fine tuned the concoction that would initiate ribosome self replication resulting in an astonishing ability to generate new ribosomes within just three hours.
Validation and Unanswered Questions:
Initially Aoki and his team questioned whether these observed results were false positives. However through repetition and thorough analysis of their experiments they consistently confirmed the authenticity of their findings. The primary question that remains is whether these generated ribosomes can undergo self replication and how many rounds of replication are possible. Aoki’s team is actively pursuing answers to these captivating inquiries.
The Path Ahead:
To fully understand how self replicating ribosomes work we need to conduct research and pinpoint the elements, in the E. Coli cell extract that are crucial for the replication process. Nonetheless this accomplishment represents a progress, in the realm of biology.
The Impact and Beyond:
According to Kate Adamala, a researcher, from the University of Minnesota this achievement is an engineering feat with reaching implications. It goes beyond creating cells and provides profound insights into the very origins of life. This breakthrough aligns well with the words of theoretical physicist Richard Feynman, who once said, “If I can’t create it I don’t understand it.”
Exploring New Frontiers:
As we delve deeper into this groundbreaking research we realize that its implications are extensive and span across fields of science and technology. Lets take a look at some aspects of this breakthrough and the potential consequences it may have;
1. Unraveling Lifes Beginnings: Understanding how ribosomes. The essential building blocks of life. Can self replicate without being confined to an environment provides insights into how life originated on our planet. It challenges existing theories. Opens up avenues for exploring the fundamental processes that sparked life.
2. Advancements in Biotechnology: The ability to create self replicating ribosomes holds promise, for biotechnology. It could lead to research tools and therapies that revolutionize treatments, drug development practices and even biofuel production methods.
3. Artificial Cell Construction: The construction of cells of self replication is now closer, to becoming a reality. These man made cells have the potential to be used in applications like targeted drug delivery and bioremediation.
4. Complexity of Ribosomes: The complexity of ribosomes is truly remarkable within the realm of biology. Creating ribosomes in a controlled environment signifies an accomplishment that showcases ingenuity. This achievement could also pave the way for understanding and manipulation of intricate biological systems.
5. The Power of Collaboration: This breakthrough emphasizes the significance of collaboration among experts from fields such as biology, chemistry and AI. By combining knowledge and skills scientists have achieved groundbreaking results in the field of science.
Conclusion:
The successful creation of self replicating ribosomes outside living cells represents a milestone in biology and biotechnology. It not offers insights into the origins of life. Also holds immense potential for transformative advancements, across scientific disciplines. As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding self replication we stand on the cusp of witnessing breakthroughs that will shape medicine, technology and our understanding of life itself.
This groundbreaking research exemplifies the essence of curiosity and ingenuity serving as a testament, to our potential for creation and comprehension, in the realm of exploration.
