
The theory known as the Snowball Earth Hypothesis captivates us with its idea of our planets past. According to this hypothesis Earth experienced two instances, between 2.4 billion and 580 million years ago when it transformed into a world. During these episodes the entire planet, including its oceans was completely covered in ice from pole to pole. This captivating theory sheds light on our history while still leaving questions unanswered. In this article we will explore the Snowball Earth Hypothesis in detail and also consider an alternative perspective called the “Slushball Earth” hypothesis.
Unveiling the Hypothesis
Back in 1992 American geologist Joseph Krschvink introduced the concept of a “Snowball Earth.” This radical idea proposes that at points in Earths history our planet experienced a cooling event that resulted in a deep freeze. During these periods ice blanketed our world from the poles to the equator. Even covered the vast expanses of its oceans. While it may seem fetched at glance the Snowball Earth Hypothesis offers a potential explanation for deposits that scientists believe originated from glaciers and have been discovered in areas that were once, near the equator.
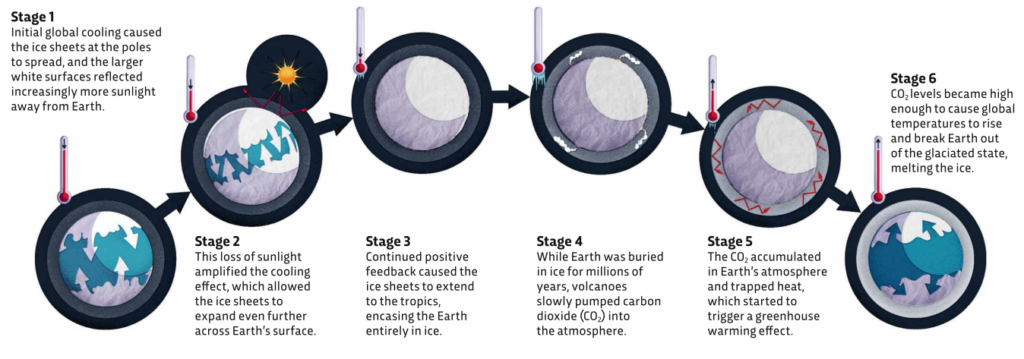
The Driving Mechanism: Ice Albedo Feedback
The theory of Snowball Earth relies on a climate mechanism called the ice albedo feedback. This complex feedback loop highlights how Earths climate system is interconnected. Here’s how it works; As the planet cools down and ice starts to expand its surface becomes more reflective. Ice has a reflectivity (albedo) compared to land or open ocean which means it reflects solar radiation back, into space. As a result solar energy is absorbed, leading to cooling. This cooling then contributes to ice growth creating a self sustaining cycle of refrigeration.
The Debate of Ideas
While the Snowball Earth theory presents a story about our planets past it is not without controversy. Within the community this hypothesis has sparked debates and alternative viewpoints. Some experts remain skeptical about the idea that our planet was completely frozen during these proposed Snowball Earth periods.
The “Slushball Earth” Hypothesis
One of the challengers, to the Snowball Earth Hypothesis is the ” Earth” hypothesis. This alternative perspective suggests that Earth might not have been entirely covered in ice during the suspected Snowball events but instead existed in a state.
In this scenario a significant portion of the Earths surface would still be frozen. There could have been areas of water particularly, around the equator and mid latitudes. This alternative theory recognizes that global glaciation may have occurred but suggests that not all regions would have been covered in ice.
Revisiting Earth’s Enigmatic Past
Unraveling the enigmas of Earths history is a complex undertaking. The ongoing debate between the Snowball Earth and slushball Earth hypotheses serves as evidence of the challenges involved in understanding our planets past. Scientific inquiry consistently prompts us to reassess our understanding of what Earth was like billions of years
Implications and Significance
Whether fully accepted or not the Snowball Earth Hypothesis emphasizes how dynamic and ever changing our planets climate has been. It serves as a reminder that Earth has undergone transformations shaping its geology, ecosystems and conditions for life itself. By studying these events we gain valuable insights, into the resilience and adaptability of our planet.
Future Research and Exploration
The ongoing debate surrounding Snowball Earth and its alternative theories continues to drive research and exploration efforts. Scientists are actively seeking evidence, refining climate models. Deepening our understanding of our planets past.
The discoveries made through these investigations have the potential to provide insights into the context of Earths climate and how it might change in the future.
Conclusion
The Snowball Earth Hypothesis presents a glimpse into the past of our planet suggesting periods of intense cooling and global glaciation. While this theory has sparked discussions and alternative perspectives such, as the Earth hypothesis it highlights the nature of Earths climate and our ongoing pursuit of scientific knowledge. The history of Earths climate remains a puzzle, with pieces missing waiting to be explored and unraveled by scientists and researchers.
